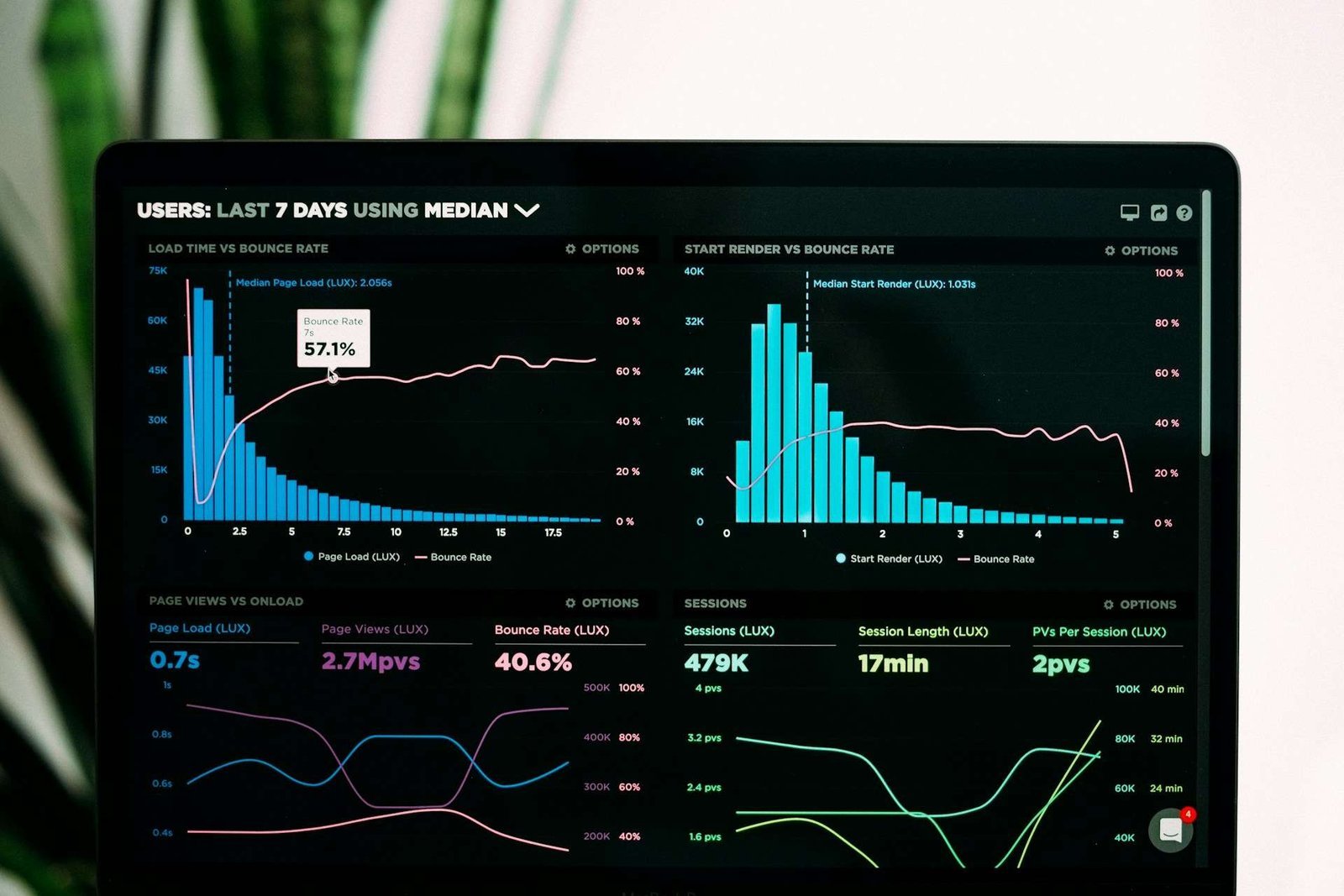
In today’s highly competitive marketplace, understanding consumer behavior has become crucial for businesses aiming to drive sales and achieve long-term success. Consumer behavior encompasses the study of how individuals make decisions to spend their available resources, such as time and money, on consumption-related items. It delves into the what, why, when, and how of consumer purchase decisions, providing valuable insights that can guide businesses in formulating effective marketing strategies.
By comprehending the underlying motivations, needs, and desires of consumers, businesses can tailor their products, services, and marketing efforts to meet and exceed customer expectations. This not only fosters customer satisfaction and loyalty but also enhances the overall brand reputation and profitability. In this blog post, we will explore the various facets of consumer behavior, its significance, and how businesses can leverage this knowledge to drive sales.

The Importance of Understanding Consumer Behavior
Enhancing Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty
Understanding consumer behavior enables businesses to identify and meet customer needs effectively. By analyzing consumer preferences, businesses can develop products and services that align with customer expectations, thereby enhancing customer satisfaction. Satisfied customers are more likely to become repeat buyers and brand advocates, contributing to long-term loyalty and positive word-of-mouth.
Targeted Marketing and Personalization
Consumer behavior insights allow businesses to segment their target audience accurately. This segmentation helps in creating targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific customer groups. Personalization, driven by consumer behavior data, ensures that marketing messages are relevant and engaging, increasing the likelihood of conversion and sales.
Optimizing Product Development
By understanding consumer preferences, businesses can make informed decisions during the product development process. This includes identifying features and attributes that are most important to consumers, as well as spotting potential gaps in the market. Consequently, businesses can develop products that are more likely to succeed, reducing the risk of product failure.

Efficient Resource Allocation
Knowledge of consumer behavior helps businesses allocate resources more efficiently. Marketing budgets can be optimized by focusing on channels and strategies that have proven to be effective in reaching and engaging the target audience. This ensures that resources are not wasted on ineffective marketing efforts.
Competitive Advantage
Businesses that invest in understanding consumer behavior gain a competitive edge in the market. By staying attuned to changing consumer trends and preferences, companies can adapt their strategies quickly and stay ahead of competitors. This agility is particularly important in dynamic industries where consumer preferences can shift rapidly.
Key Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
Psychological Factors
Motivation
Motivation is the driving force behind consumer actions. It stems from the recognition of a need or desire that requires fulfillment. Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a widely used framework for understanding motivation. It categorizes human needs into five levels: physiological, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization. Consumers are motivated to fulfill needs at each level, and businesses can tailor their marketing strategies to address these needs effectively.

Perception
Perception is how consumers interpret and make sense of the information they receive. It is influenced by individual experiences, beliefs, and attitudes. Marketers need to understand how consumers perceive their products and brand, as perception can significantly impact purchase decisions. Creating positive perceptions through branding, advertising, and customer experiences is crucial for driving sales.
Learning
Learning involves changes in consumer behavior arising from experiences. It encompasses how consumers acquire information about products and services, and how they apply this knowledge to future purchase decisions. Businesses can leverage learning theories, such as classical conditioning and operant conditioning, to influence consumer behavior. For example, offering rewards and incentives can reinforce positive buying behaviors.
Beliefs and Attitudes
Beliefs and attitudes shape how consumers evaluate products and brands. Beliefs are convictions that consumers hold about specific products or brands, while attitudes are overall evaluations that can be positive or negative. Marketers need to understand the beliefs and attitudes of their target audience to craft messages that resonate and persuade consumers to choose their products.

Social Factors
Family
Family plays a significant role in shaping consumer behavior. Family members influence each other’s purchase decisions, particularly in the case of products and services used by the entire household. Understanding the dynamics of family decision-making can help businesses target their marketing efforts more effectively.
Social Groups
Social groups, including friends, colleagues, and reference groups, impact consumer behavior. Consumers often seek opinions and recommendations from their social groups before making purchase decisions. Businesses can leverage social proof and influencer marketing to tap into the influence of social groups and drive sales.
Social Status
Social status and the desire for status symbols influence consumer behavior. Consumers may purchase products that reflect their social status or aspirations. Luxury brands, for example, capitalize on this by positioning their products as status symbols. Understanding the social aspirations of the target audience can help businesses position their products appropriately.

Personal Factors
Age and Life Cycle Stage
Consumer needs and preferences change with age and life cycle stage. For example, the purchasing behavior of teenagers differs significantly from that of middle-aged adults. Businesses need to consider the age and life cycle stage of their target audience when developing marketing strategies and product offerings.
Occupation
Occupation influences income levels and purchasing power, which in turn affects consumer behavior. Professionals in different occupations have varying needs and preferences. Businesses can segment their target audience based on occupation to tailor their marketing efforts effectively.
Lifestyle
Lifestyle reflects an individual’s activities, interests, and opinions. It encompasses how consumers spend their time and money. Understanding the lifestyle of the target audience helps businesses create marketing messages and product offerings that align with consumer values and preferences.

Cultural Factors
Culture
Culture encompasses the shared values, beliefs, and customs of a society. It plays a significant role in shaping consumer behavior. Businesses need to understand the cultural context of their target audience to create culturally relevant marketing campaigns and products.
Subculture
Subcultures are groups within a larger culture that have distinct values, beliefs, and behaviors. Examples include ethnic groups, religious communities, and regional populations. Identifying and targeting subcultures can help businesses tap into niche markets and cater to specific consumer needs.
Social Class
Social class is determined by factors such as income, education, and occupation. It influences consumer preferences and purchasing behavior. Businesses can segment their target audience based on social class to create marketing strategies that resonate with different consumer segments.

Analyzing Consumer Behavior
Market Research
Market research is a systematic process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data about consumers and the market. It helps businesses understand consumer needs, preferences, and behavior. Market research can be conducted through various methods, including surveys, interviews, focus groups, and observation.
Surveys and Questionnaires
Surveys and questionnaires are widely used to gather quantitative data from a large number of respondents. They can provide insights into consumer preferences, attitudes, and buying behavior. Businesses can use online surveys, telephone surveys, or face-to-face interviews to collect data.
Focus Groups
Focus groups involve small groups of consumers who discuss specific topics or products under the guidance of a moderator. This qualitative research method provides in-depth insights into consumer attitudes, perceptions, and motivations. Focus groups are particularly useful for exploring new product ideas and gathering feedback on marketing campaigns.
Observation
Observation involves watching and recording consumer behavior in natural settings. This method provides real-time insights into how consumers interact with products and make purchase decisions. Businesses can use techniques such as ethnographic research and mystery shopping to observe consumer behavior.

Consumer Analytics
Consumer analytics involves the use of data and statistical methods to analyze consumer behavior. It leverages data from various sources, such as transaction records, website analytics, and social media, to identify patterns and trends. Consumer analytics can provide valuable insights for predicting future behavior and optimizing marketing strategies.
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics uses historical data and statistical models to forecast future consumer behavior. It can help businesses identify potential customers, predict purchase patterns, and personalize marketing efforts. By understanding what consumers are likely to buy, businesses can tailor their product offerings and promotions to drive sales.
Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation involves dividing the target audience into distinct groups based on shared characteristics. This can include demographic factors, such as age and income, as well as behavioral factors, such as purchase history and product preferences. Segmentation allows businesses to create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific customer groups.
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis involves analyzing text data, such as customer reviews and social media posts, to determine consumer sentiment. It helps businesses understand how consumers feel about their products and brand. Positive sentiment can be leveraged to build brand loyalty, while negative sentiment can highlight areas for improvement.

Strategies for Driving Sales Through Understanding Consumer Behavior
Personalized Marketing
Personalized marketing involves tailoring marketing messages and offers to individual consumers based on their preferences and behavior. It creates a more relevant and engaging experience, increasing the likelihood of conversion and sales.
Personalized Emails
Email marketing remains a powerful tool for reaching consumers. By leveraging consumer data, businesses can send personalized emails that include product recommendations, special offers, and personalized content. This can significantly improve open and click-through rates, driving sales.
Dynamic Content
Dynamic content involves creating website and app experiences that adapt to individual users. This can include personalized product recommendations, customized landing pages, and tailored promotions. Dynamic content enhances the user experience and encourages consumers to make purchases.
Behavioral Targeting
Behavioral targeting involves delivering ads and content to consumers based on their past behavior. This includes their browsing history, purchase history, and interactions with the brand.

Retargeting
Retargeting involves showing ads to consumers who have previously visited the company’s website or interacted with the brand. It keeps the brand top of mind and encourages consumers to return and complete their purchase. Retargeting can be done through display ads, social media ads, and email marketing.
Lookalike Audiences
Lookalike audiences are groups of consumers who share similar characteristics with existing customers. By targeting lookalike audiences, businesses can reach potential customers who are likely to be interested in their products. This strategy leverages consumer behavior data to expand the customer base and drive sales.
Social Proof and Influencer Marketing
Social proof is the psychological phenomenon where people look to others to determine what is correct or desirable. Businesses can leverage social proof to influence consumer behavior and drive sales.
Customer Reviews and Testimonials
Customer reviews and testimonials provide social proof by showcasing the positive experiences of other consumers. Encouraging satisfied customers to leave reviews and share testimonials can build trust and credibility, influencing potential buyers to make a purchase.

Influencer Partnerships
Influencers have a significant impact on consumer behavior, particularly on social media platforms. Partnering with influencers who align with the brand can help businesses reach a larger audience and build credibility. Influencers can create authentic content that resonates with their followers, driving traffic and sales.
Omnichannel Experience
An omnichannel experience ensures that consumers have a seamless and consistent experience across all touchpoints, whether online or offline. This approach caters to the modern consumer’s expectation of being able to interact with the brand through multiple channels.
Integrated Marketing Campaigns
Integrated marketing campaigns involve coordinating marketing efforts across various channels, such as social media, email, and in-store promotions. Consistent messaging and branding across channels create a cohesive experience that enhances consumer engagement and drives sales.
Unified Customer Data
Unified customer data provides a holistic view of each customer by integrating data from different sources. This enables businesses to understand the complete customer journey and deliver personalized experiences. A unified approach to customer data helps in creating targeted marketing strategies that resonate with consumers.

Loyalty Programs
Loyalty programs reward repeat customers and encourage long-term loyalty. By understanding consumer behavior, businesses can design loyalty programs that resonate with their target audience.
Point-Based Systems
Point-based loyalty programs reward customers with points for every purchase, which can be redeemed for discounts or free products. This incentivizes repeat purchases and encourages customers to spend more.
Tiered Programs
Tiered loyalty programs offer different levels of rewards based on the customer’s spending. Higher tiers provide more exclusive benefits, motivating customers to increase their spending to reach the next level. This approach leverages consumer behavior by creating a sense of achievement and exclusivity.
Conclusion
Understanding consumer behavior is the cornerstone of effective marketing and sales strategies. By delving into the psychological, social, personal, and cultural factors that influence consumer decisions, businesses can create targeted and personalized experiences that resonate with their audience. Market research and consumer analytics provide valuable insights into consumer preferences and behavior, enabling businesses to make informed decisions and optimize their marketing efforts.
Implementing strategies such as personalized marketing, behavioral targeting, social proof, omnichannel experiences, and loyalty programs can drive sales and foster long-term customer loyalty. As the marketplace continues to evolve, businesses that prioritize understanding and responding to consumer behavior will be well-positioned to thrive and achieve sustainable success.
By investing in the study of consumer behavior and continuously adapting to changing consumer trends, businesses can build strong connections with their customers, enhance their brand reputation, and ultimately drive sales growth. Understanding consumer behavior is not just a one-time effort but an ongoing process that requires dedication and a willingness to innovate and adapt. In doing so, businesses can create meaningful and lasting relationships with their customers, ensuring their continued success in the competitive marketplace.