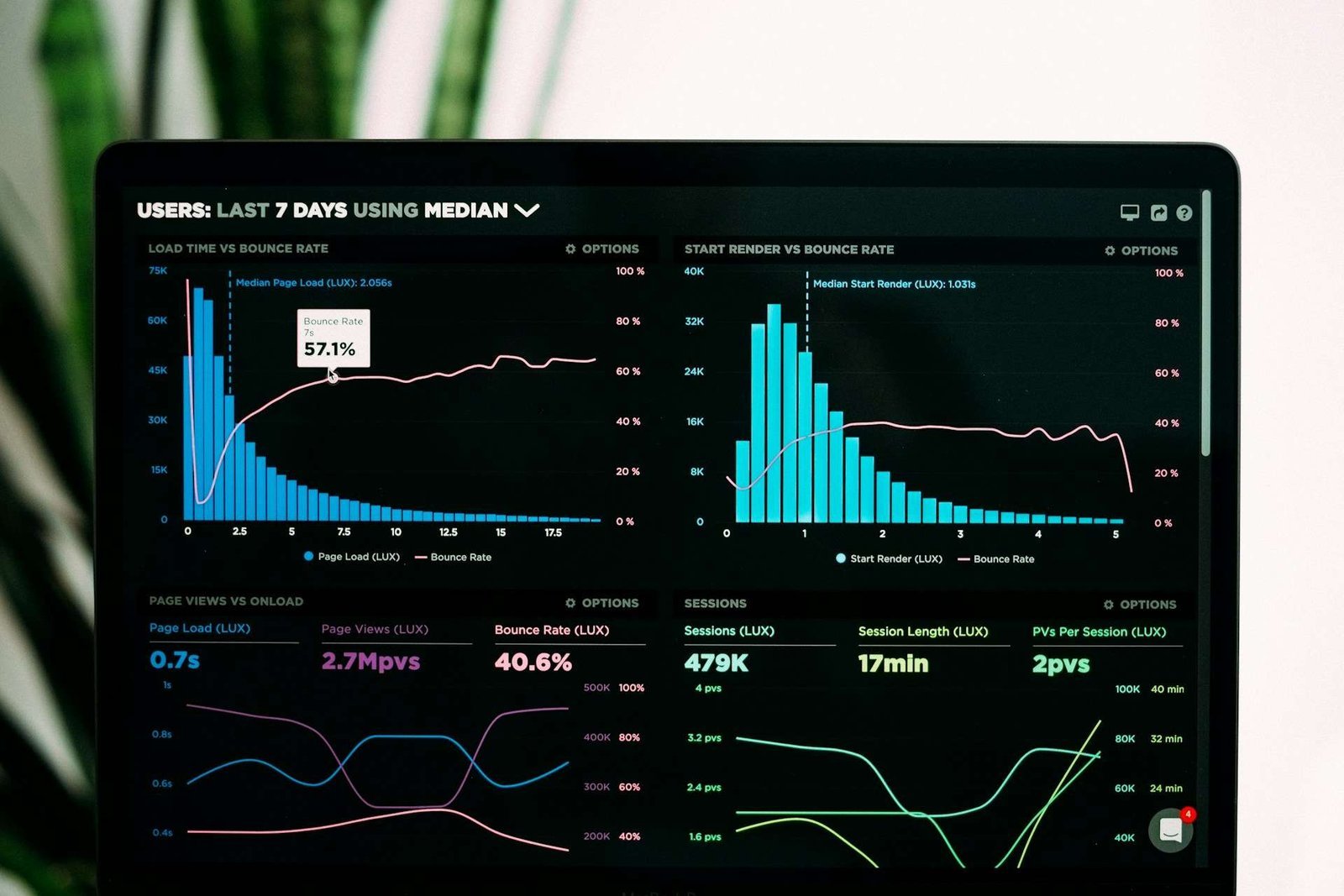
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transformed from a futuristic concept into a present-day reality, significantly reshaping various sectors. Among its many applications, business automation stands out as a domain where AI’s impact has been profoundly transformative. This blog post explores the rise of AI in business automation, detailing its evolution, applications, benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
Understanding AI and Business Automation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, particularly computer systems. These processes include learning (the acquisition of information and rules for using the information), reasoning (using rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions), and self-correction. Specific applications of AI include expert systems, natural language processing (NLP), speech recognition, and machine vision.
Business Automation, on the other hand, involves the use of technology to perform tasks without human intervention. It aims to streamline processes, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. The integration of AI into business automation has given rise to more sophisticated systems that not only perform repetitive tasks but also make informed decisions, learn from data, and adapt to new situations.

Evolution of AI in Business Automation
The journey of AI in business automation can be traced through several stages:
- Early Days of Automation (1950s-1980s):
- Initially, automation focused on simple repetitive tasks in manufacturing through mechanization and assembly lines.
- The advent of computers brought about basic automation in data processing and administrative tasks.
- Emergence of AI (1980s-2000s):
- AI began to gain traction with advancements in computing power and data availability.
- Expert systems, which mimic the decision-making abilities of a human expert, were among the first AI applications in business.
- The development of machine learning algorithms allowed systems to improve performance with experience.
- AI Integration (2000s-2010s):
- The rise of big data and advancements in machine learning led to more sophisticated AI applications.
- AI started being integrated into customer relationship management (CRM), supply chain management, and other business processes.
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA) emerged, using AI to automate routine, rule-based tasks across various sectors.
- Current Landscape (2010s-Present):
- AI has become integral to many business operations, driving efficiency and innovation.
- The use of AI spans across various functions, from predictive analytics and personalized marketing to advanced robotics and autonomous systems.
- AI technologies such as natural language processing, computer vision, and deep learning are at the forefront of automation.

Key Applications of AI in Business Automation
1. Robotic Process Automation (RPA):
- RPA uses AI to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks such as data entry, invoice processing, and customer support.
- It improves accuracy, reduces costs, and frees up employees to focus on more strategic tasks.
2. Customer Service and Support:
- AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide 24/7 customer support, handling queries, processing orders, and resolving issues.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables these systems to understand and respond to customer queries in real-time.
3. Supply Chain Management:
- AI optimizes supply chain operations through demand forecasting, inventory management, and logistics planning.
- Machine learning algorithms analyze historical data to predict demand, ensuring optimal stock levels and reducing waste.
4. Marketing and Sales:
- AI-driven analytics provide insights into customer behavior, enabling personalized marketing campaigns.
- Predictive analytics helps identify potential leads, improving sales efficiency and conversion rates.

5. Human Resources:
- AI automates recruitment processes by screening resumes, scheduling interviews, and conducting initial assessments.
- Employee performance management systems use AI to provide feedback, identify training needs, and predict turnover.
6. Financial Services:
- AI detects fraudulent activities by analyzing transaction patterns and identifying anomalies.
- Automated trading systems use AI to analyze market data and execute trades at optimal times.
7. Manufacturing:
- AI-powered robots perform complex tasks with high precision, increasing production efficiency.
- Predictive maintenance systems use AI to monitor equipment health and predict failures, reducing downtime.
Benefits of AI in Business Automation
1. Increased Efficiency and Productivity:
- AI automates repetitive tasks, allowing employees to focus on higher-value activities.
- It speeds up processes, reduces errors, and improves overall productivity.

2. Cost Savings:
- Automation reduces labor costs and operational expenses.
- AI-driven optimization minimizes waste and improves resource utilization.
3. Enhanced Decision Making:
- AI analyzes large volumes of data to provide actionable insights, supporting informed decision-making.
- Predictive analytics helps businesses anticipate trends and respond proactively.
4. Improved Customer Experience:
- AI enables personalized interactions, providing customers with relevant recommendations and support.
- Automated systems ensure timely and accurate responses, enhancing customer satisfaction.
5. Scalability:
- AI-powered systems can handle increasing workloads without compromising performance.
- Businesses can scale operations efficiently, adapting to changing demands.
6. Competitive Advantage:
- Early adopters of AI gain a competitive edge through improved efficiency, innovation, and customer engagement.
- AI-driven insights help businesses stay ahead of market trends and competitors.

Challenges of Implementing AI in Business Automation
1. High Initial Costs:
- Implementing AI solutions involves significant investment in technology, infrastructure, and training.
- Small and medium-sized enterprises may find it challenging to bear these costs.
2. Data Privacy and Security:
- AI systems rely on vast amounts of data, raising concerns about data privacy and security.
- Businesses must ensure compliance with regulations and protect sensitive information.
3. Integration with Existing Systems:
- Integrating AI with legacy systems can be complex and time-consuming.
- Businesses need to ensure seamless integration to maximize the benefits of AI.
4. Workforce Impact:
- Automation may lead to job displacement, causing concerns among employees.
- Businesses need to manage this transition by reskilling employees and creating new opportunities.

5. Ethical and Bias Issues:
- AI systems can perpetuate biases present in training data, leading to unfair outcomes.
- Ensuring ethical AI practices and addressing bias is crucial for responsible AI implementation.
6. Technological Limitations:
- Despite advancements, AI systems still have limitations in understanding context and making nuanced decisions.
- Continuous development and refinement of AI technologies are necessary.
Future Prospects of AI in Business Automation
1. Autonomous Systems:
- The development of autonomous systems, such as self-driving cars and drones, will revolutionize transportation and logistics.
- These systems will enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and open new business opportunities.
2. Advanced Personalization:
- AI will enable hyper-personalization in marketing, delivering tailored experiences based on individual preferences and behavior.
- Businesses will leverage AI to create more engaging and relevant interactions with customers.
3. Enhanced Human-Machine Collaboration:
- AI will augment human capabilities, enabling better collaboration between humans and machines.
- Businesses will adopt AI-powered tools to enhance productivity and decision-making.

4. AI in Healthcare:
- AI will play a significant role in healthcare automation, from diagnostics and treatment planning to administrative tasks.
- It will improve patient outcomes, reduce costs, and enhance the efficiency of healthcare delivery.
5. Edge Computing:
- The integration of AI with edge computing will enable real-time processing and decision-making at the edge of the network.
- This will be crucial for applications requiring low latency and real-time responses.
6. Ethical AI Development:
- As AI adoption grows, there will be a greater focus on ethical AI development, ensuring transparency, fairness, and accountability.
- Businesses will prioritize responsible AI practices to build trust and mitigate risks.
7. AI-Driven Innovation:
- AI will continue to drive innovation across industries, enabling the development of new products, services, and business models.
- Businesses will leverage AI to explore new opportunities and stay competitive.
Conclusion

The rise of artificial intelligence in business automation marks a significant milestone in the evolution of technology. AI has transcended its role as a tool for automating repetitive tasks to become a strategic enabler of business transformation. By enhancing efficiency, reducing costs, and enabling data-driven decision-making, AI is reshaping the business landscape.
However, the journey is not without challenges. Businesses must navigate the complexities of AI implementation, address ethical and bias issues, and manage the impact on the workforce. Despite these challenges, the potential benefits of AI in business automation far outweigh the risks.
As AI continues to evolve, businesses that embrace this transformative technology will be better positioned to thrive in the competitive landscape. The future of business automation lies in the seamless integration of AI, where human creativity and machine intelligence work together to drive innovation and create value.
In the words of renowned AI pioneer Andrew Ng, “AI is the new electricity.” Just as electricity revolutionized industries and transformed the world, AI is set to usher in a new era of business automation, unlocking unprecedented opportunities and shaping the future of work.