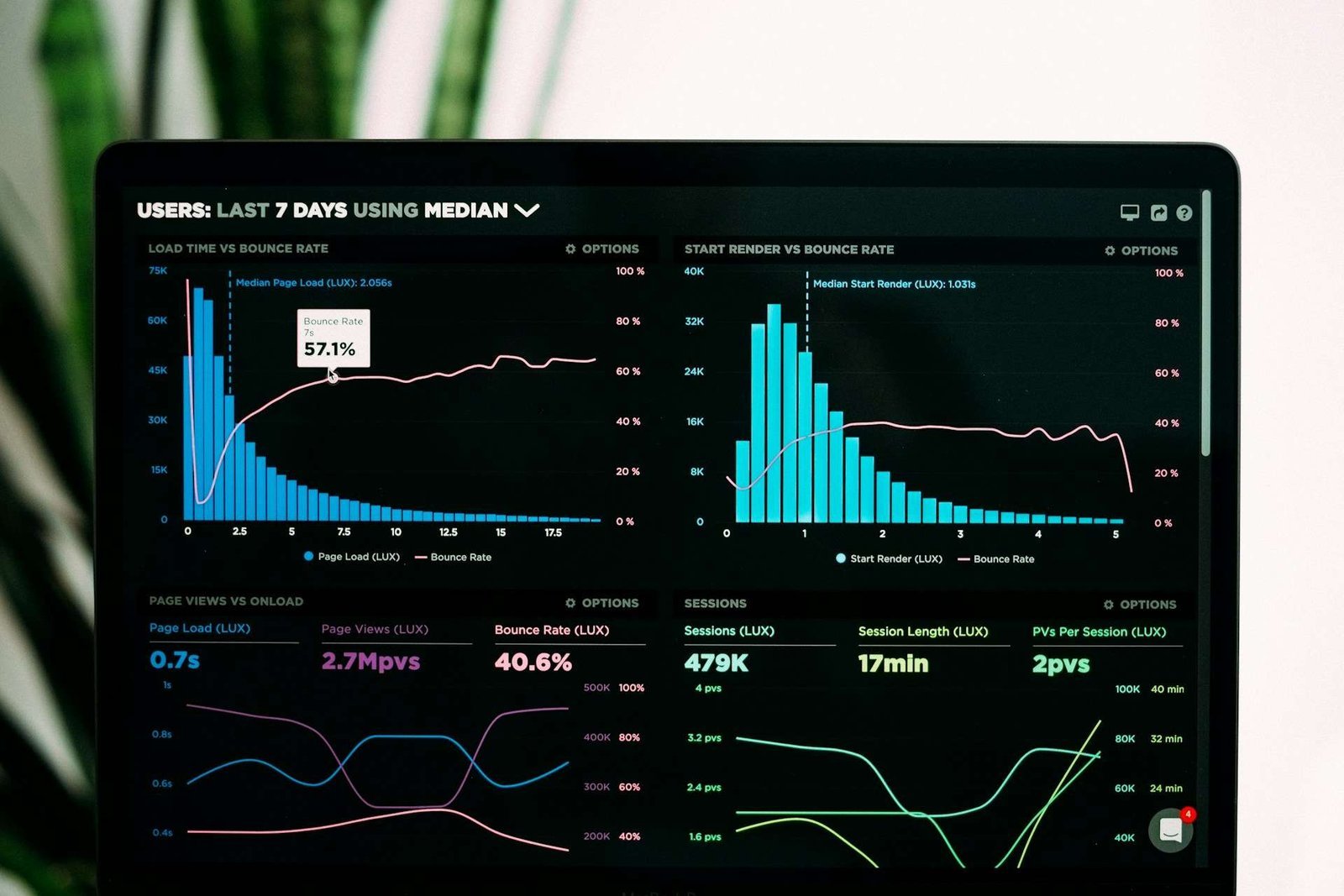
Starting a business is an exciting journey filled with potential and opportunity. However, one of the critical decisions that entrepreneurs face early on is choosing the right business model. A business model defines how your company creates, delivers, and captures value. It is the blueprint for your business’s success and sustainability. With numerous options available, understanding the different business models and their implications is essential for making an informed decision. This comprehensive guide will explore various business models, their advantages and disadvantages, and provide insights into how to choose the right one for your venture.

The Importance of Choosing the Right Business Model
Selecting the right business model is crucial for several reasons:
- Value Proposition: It defines what value you offer to your customers and how you differentiate yourself from competitors.
- Revenue Streams: It determines how your business will make money, impacting profitability and growth.
- Cost Structure: It outlines the major costs and investments needed, influencing your financial planning and sustainability.
- Customer Relationships: It shapes how you interact with and retain customers, affecting long-term success.
- Scalability: It influences how easily you can expand your business operations and enter new markets.
Making the right choice can lead to sustainable growth and profitability, while the wrong choice can hinder your progress and lead to failure.
Common Business Models
Here are some of the most common business models, along with their key characteristics, advantages, and challenges:

1. Direct Sales Model
Description: In the direct sales model, businesses sell products or services directly to consumers without intermediaries. This model is prevalent in industries such as retail, real estate, and personal services.
Advantages:
- Higher Margins: By eliminating middlemen, businesses can retain more profit.
- Control Over Customer Experience: Direct interaction with customers allows for better service and relationship management.
- Immediate Feedback: Direct contact with customers provides valuable insights for improvement.
Challenges:
- High Marketing Costs: Businesses must invest significantly in marketing to reach customers.
- Inventory Management: Managing stock levels can be complex and costly.
- Scaling Limitations: Scaling can be challenging without a robust distribution network.
2. Freemium Model
Description: The freemium model offers basic services for free while charging for premium features. This model is common in software, online services, and mobile apps.
Advantages:
- User Acquisition: Free access attracts a large user base quickly.
- Upselling Opportunities: Free users can be converted to paying customers through premium offerings.
- Brand Awareness: High user engagement increases brand visibility and market presence.
Challenges:
- Conversion Rates: Only a small percentage of users may convert to paying customers.
- Sustainability: The business must sustain free users while monetizing effectively.
- Complex Pricing Strategy: Balancing free and premium features can be challenging.

3. Subscription Model
Description: In the subscription model, customers pay a recurring fee to access a product or service. This model is widely used in industries such as media, entertainment, and software.
Advantages:
- Predictable Revenue: Recurring payments provide steady and predictable cash flow.
- Customer Retention: Continuous service fosters long-term customer relationships.
- Upselling Opportunities: Additional features or higher-tier subscriptions can boost revenue.
Challenges:
- Churn Rate: Retaining subscribers requires continuous value delivery.
- Initial Acquisition Cost: Acquiring new subscribers can be costly.
- Content or Service Quality: Maintaining high quality to justify recurring payments is crucial.
4. Marketplace Model
Description: The marketplace model connects buyers and sellers on a platform, facilitating transactions. This model is popular in e-commerce, real estate, and freelance services.
Advantages:
- Scalability: Marketplaces can grow rapidly with minimal inventory or infrastructure.
- Diverse Revenue Streams: Revenue can come from transaction fees, subscriptions, advertising, etc.
- Network Effects: The platform’s value increases as more users join, attracting more buyers and sellers.
Challenges:
- Trust and Safety: Ensuring trust and safety on the platform is essential.
- Competition: Marketplaces often face intense competition and price wars.
- Regulation and Compliance: Navigating regulatory requirements can be complex.

5. Affiliate Model
Description: In the affiliate model, businesses reward affiliates for driving traffic or sales through their marketing efforts. This model is common in online retail and digital marketing.
Advantages:
- Low Risk: Businesses pay only for actual sales or leads generated.
- Extended Reach: Affiliates can significantly expand your marketing reach.
- Performance-Based: Costs are directly tied to performance, improving ROI.
Challenges:
- Quality Control: Ensuring affiliates represent your brand accurately can be difficult.
- Dependency: Over-reliance on affiliates can be risky if they shift focus.
- Commission Management: Tracking and managing commissions can be complex.
6. Franchise Model
Description: The franchise model allows entrepreneurs to operate their own business using the branding, products, and support of an established company. This model is prevalent in the food, retail, and service industries.
Advantages:
- Brand Recognition: Franchisees benefit from established brand recognition and reputation.
- Support and Training: Franchisors provide extensive support, training, and resources.
- Proven Business Model: Franchises operate using a tested and proven business model.
Challenges:
- Initial Investment: High upfront costs for franchise fees and setup.
- Operational Restrictions: Franchisees must adhere to strict operational guidelines.
- Profit Sharing: Ongoing royalties and fees reduce profit margins.

7. On-Demand Model
Description: The on-demand model provides immediate access to products or services through digital platforms. This model is common in transportation, food delivery, and personal services.
Advantages:
- Convenience: Meets the demand for quick and convenient access to services.
- Scalability: Technology enables rapid scaling and geographic expansion.
- Customer Insights: Data collection provides valuable insights into customer preferences.
Challenges:
- Operational Complexity: Coordinating logistics and service delivery can be challenging.
- Competition: High competition in popular on-demand sectors.
- Regulatory Issues: Compliance with local regulations can be complex and costly.
8. Licensing Model
Description: The licensing model involves granting permission to another company to produce and sell your products or use your intellectual property. This model is prevalent in technology, entertainment, and fashion industries.
Advantages:
- Revenue Streams: Licensing can generate additional revenue without significant investment.
- Brand Expansion: Licensing allows for brand expansion into new markets and product lines.
- Risk Mitigation: Licensees assume production and market risks.
Challenges:
- Quality Control: Ensuring licensed products meet brand standards can be challenging.
- Negotiation Complexity: Licensing agreements can be complex and require careful negotiation.
- Dependency: Dependence on licensees for market success can be risky.

9. Manufacturing Model
Description: In the manufacturing model, businesses produce goods for sale to other businesses or consumers. This model is common in industries such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods.
Advantages:
- Control Over Production: Direct control over quality and production processes.
- Economies of Scale: Large-scale production can lead to cost savings and higher margins.
- Innovation Opportunities: Ability to innovate and develop new products.
Challenges:
- High Capital Investment: Significant investment in machinery, facilities, and workforce.
- Inventory Management: Managing raw materials and finished goods inventory.
- Market Demand: Fluctuating market demand can impact production and profitability.
10. Brokerage Model
Description: The brokerage model involves facilitating transactions between buyers and sellers, earning a commission or fee for each transaction. This model is common in real estate, finance, and travel industries.
Advantages:
- Revenue Potential: High revenue potential from commissions on large transactions.
- Market Expertise: Brokers can leverage market knowledge and expertise.
- Scalability: Ability to scale by expanding the network of buyers and sellers.
Challenges:
- Market Dependency: Revenue is dependent on market conditions and transaction volumes.
- Competition: Intense competition from other brokers and platforms.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating regulatory requirements can be complex.

How to Choose the Right Business Model
Selecting the right business model involves a thorough analysis of your business goals, market conditions, and resources. Here are key steps to guide your decision-making process:
1. Understand Your Value Proposition
Identify what makes your business unique and valuable to customers. Consider the following questions:
- What problem does your product or service solve?
- What benefits do you offer that competitors do not?
- How do you differentiate yourself in the market?
2. Analyze Your Target Market
Understanding your target market is crucial for selecting a business model that aligns with customer needs and preferences. Conduct market research to gather insights on:
- Customer demographics and behavior
- Market size and growth potential
- Competitive landscape and trends
3. Evaluate Revenue Potential
Assess the revenue potential of different business models to determine which one aligns with your financial goals. Consider factors such as:
- Pricing strategy and profit margins
- Revenue streams and scalability
- Long-term growth and sustainability

4. Consider Cost Structure
Analyze the cost structure associated with each business model to ensure it aligns with your financial resources and capabilities. Key considerations include:
- Initial and ongoing investment requirements
- Fixed and variable costs
- Cost of customer acquisition and retention
5. Assess Scalability
Evaluate how easily each business model can scale as your business grows. Consider the following:
- Infrastructure and resource requirements
- Market expansion opportunities
- Potential challenges and risks associated with scaling
6. Examine Customer Relationships
Consider how each business model impacts your relationship with customers. Think about:
- Customer acquisition and retention strategies
- Customer engagement and support
- Brand loyalty and advocacy
7. Evaluate Competitive Advantage
Determine how each business model can help you achieve and maintain a competitive advantage. Consider factors such as:
- Barriers to entry for competitors
- Intellectual property and innovation
- Brand strength and reputation

8. Test and Iterate
Before fully committing to a business model, consider testing it on a smaller scale to gather feedback and make adjustments. This approach allows you to validate assumptions and refine your strategy based on real-world data.
Case Studies: Successful Business Models in Action
1. Airbnb: Marketplace Model
Airbnb revolutionized the hospitality industry with its marketplace model, connecting travelers with hosts offering unique accommodations. Key factors in Airbnb’s success include:
- Scalability: Rapid global expansion with minimal physical assets.
- Network Effects: Increasing value as more users joined the platform.
- Trust and Safety: Implementation of review systems and safety protocols.
2. Netflix: Subscription Model
Netflix transformed the entertainment industry with its subscription-based streaming service. Key elements of Netflix’s success include:
- Predictable Revenue: Recurring subscriptions providing steady cash flow.
- Customer Retention: High-quality content and personalized recommendations.
- Global Reach: Expansion into international markets and original content production.

3. Uber: On-Demand Model
Uber disrupted the transportation industry with its on-demand ride-hailing service. Key elements of Uber’s success include:
- Scalability: Rapid geographic expansion and diversification of services.
- Convenience: Easy access to rides through a user-friendly app.
- Data Insights: Utilization of data to optimize operations and improve customer experience.
4. Salesforce: SaaS Model
Salesforce pioneered the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model, offering cloud-based CRM solutions. Key factors in Salesforce’s success include:
- Recurring Revenue: Subscription-based model ensuring predictable income.
- Customer Success: Focus on customer success and support.
- Innovation: Continuous development of new features and integrations.
Conclusion
Choosing the right business model is a critical decision that can significantly impact your venture’s success. By understanding the various business models, evaluating your value proposition, target market, revenue potential, cost structure, scalability, customer relationships, and competitive advantage, you can make an informed choice that aligns with your business goals. Remember, the business landscape is dynamic, and flexibility is key. Be prepared to adapt and iterate your business model as needed to stay competitive and achieve long-term success.
Embarking on your entrepreneurial journey with a well-thought-out business model sets the foundation for growth and sustainability. Whether you’re starting a new venture or pivoting an existing one, the right business model will guide you towards achieving your vision and making a meaningful impact in your industry.