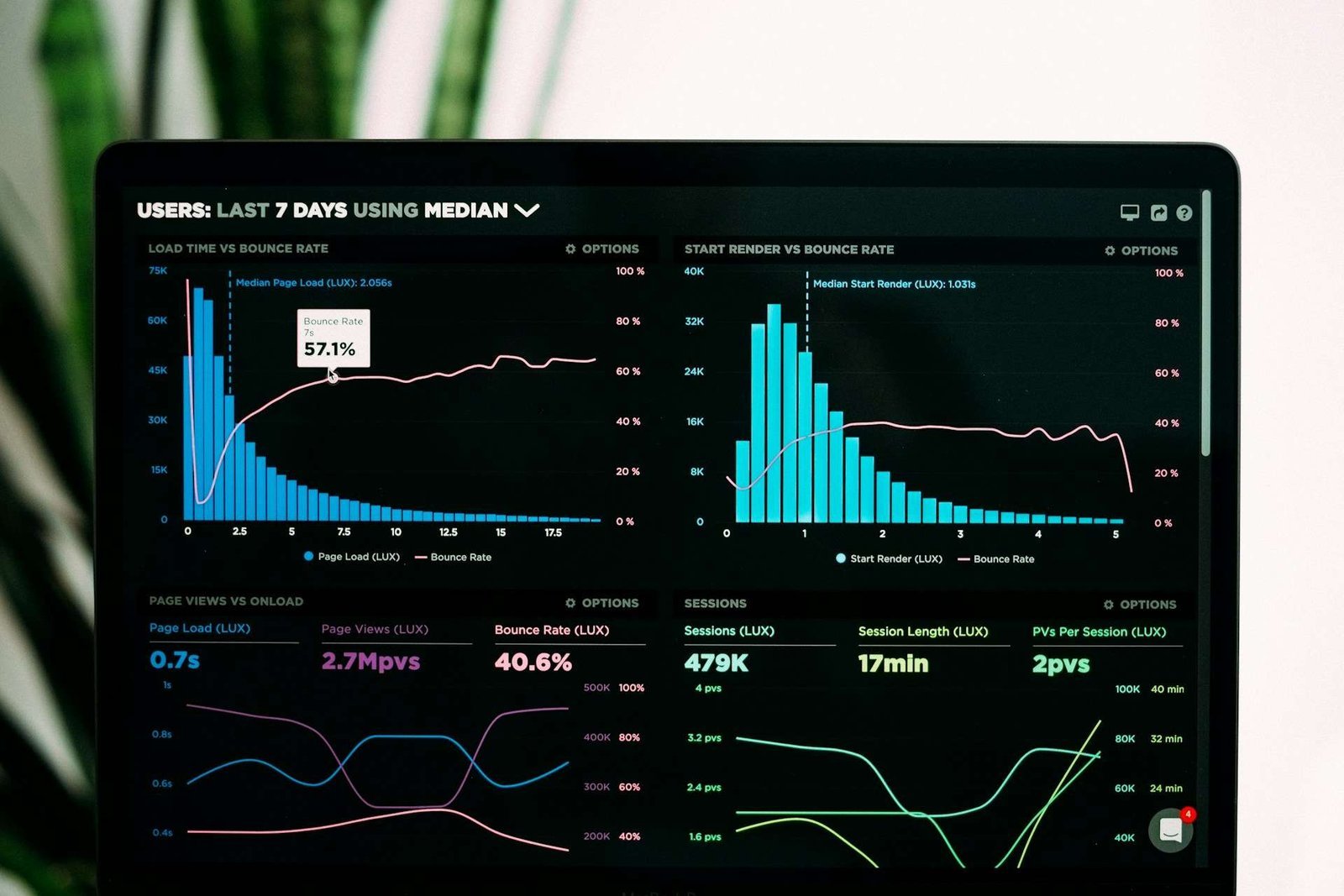
Supply chain management (SCM) is the backbone of modern commerce. It involves the coordination of all parties, processes, and technologies involved in producing and delivering goods and services to consumers. Effective SCM ensures that products are delivered to the right place, at the right time, in the right quantity, and at the right cost. However, managing a supply chain is fraught with challenges, ranging from demand fluctuations to global disruptions. This blog post explores these challenges and provides strategies to overcome them.

The Importance of Supply Chain Management
Before diving into the challenges, it’s important to understand why SCM is crucial for businesses:
- Customer Satisfaction: Timely delivery of products is critical for maintaining customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Cost Efficiency: Effective SCM can significantly reduce operational costs through optimized processes and reduced waste.
- Competitive Advantage: Companies with efficient supply chains can respond more quickly to market changes, giving them a competitive edge.
- Risk Management: A well-managed supply chain can better anticipate and mitigate risks, from supplier failures to geopolitical issues.
Major Challenges in Supply Chain Management
1. Demand Forecasting and Inventory Management
Challenge: Accurate demand forecasting is essential for maintaining optimal inventory levels. Overestimating demand leads to excess inventory and increased holding costs, while underestimating demand can result in stockouts and lost sales.
Solutions:
- Advanced Analytics: Utilizing predictive analytics and machine learning can improve forecasting accuracy by analyzing historical data and identifying patterns.
- Collaborative Planning: Engaging in collaborative planning, forecasting, and replenishment (CPFR) with suppliers and customers ensures better alignment and sharing of information.
- Flexible Inventory Strategies: Implementing strategies like just-in-time (JIT) and safety stock can help balance inventory levels according to fluctuating demand.

2. Supply Chain Visibility
Challenge: Lack of visibility across the supply chain can lead to inefficiencies and disruptions. Without real-time information, companies cannot respond quickly to changes or issues.
Solutions:
- IoT and RFID Technologies: Implementing Internet of Things (IoT) devices and Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags can provide real-time tracking of goods and assets throughout the supply chain.
- Integrated IT Systems: Using integrated supply chain management software that consolidates data from various sources enhances visibility and facilitates better decision-making.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology can provide a secure and transparent ledger of transactions, improving traceability and accountability across the supply chain.
3. Globalization and Geopolitical Risks
Challenge: Global supply chains are exposed to geopolitical risks, such as trade wars, tariffs, and political instability. These factors can disrupt the flow of goods and increase costs.
Solutions:
- Diversification of Suppliers: Reducing dependency on a single supplier or region by diversifying the supplier base can mitigate risks associated with geopolitical events.
- Nearshoring and Reshoring: Moving production closer to the end market (nearshoring) or bringing it back to the home country (reshoring) can reduce geopolitical risks and improve supply chain resilience.
- Scenario Planning: Conducting scenario planning and risk assessments helps companies prepare for various geopolitical events and develop contingency plans.

4. Supplier Relationship Management
Challenge: Building and maintaining strong relationships with suppliers is critical for ensuring the smooth operation of the supply chain. Poor supplier relationships can lead to quality issues, delays, and increased costs.
Solutions:
- Strategic Partnerships: Developing strategic partnerships with key suppliers fosters collaboration and long-term commitment.
- Performance Metrics: Establishing clear performance metrics and regularly evaluating supplier performance ensures that suppliers meet the required standards.
- Communication and Collaboration: Maintaining open lines of communication and collaborating on process improvements can enhance supplier relationships and performance.
5. Logistics and Transportation Management
Challenge: Efficiently managing logistics and transportation is essential for timely delivery and cost control. Challenges include rising fuel costs, driver shortages, and transportation disruptions.
Solutions:
- Route Optimization: Using advanced routing software to optimize delivery routes can reduce transportation costs and improve delivery times.
- Multi-Modal Transportation: Leveraging multiple modes of transportation (e.g., road, rail, sea, air) provides flexibility and can reduce dependency on any single mode.
- Sustainable Practices: Implementing sustainable practices, such as using energy-efficient vehicles and optimizing load capacity, can reduce costs and environmental impact.

6. Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Challenge: Navigating complex and ever-changing regulatory requirements is a significant challenge for supply chain managers. Non-compliance can result in fines, delays, and reputational damage.
Solutions:
- Automated Compliance Systems: Using automated compliance management systems can help ensure adherence to regulations and reduce the risk of human error.
- Continuous Training: Regularly training staff on regulatory requirements and compliance best practices keeps everyone informed and prepared.
- Regulatory Intelligence: Staying informed about regulatory changes and trends through regulatory intelligence services enables proactive compliance management.
7. Technological Advancements
Challenge: Keeping up with rapid technological advancements and integrating new technologies into existing supply chain systems can be daunting and expensive.
Solutions:
- Adopting Agile Methodologies: Using agile methodologies for technology implementation allows for incremental changes and reduces the risk of disruption.
- Scalable Solutions: Investing in scalable technology solutions that can grow and adapt to changing needs ensures long-term viability.
- Continuous Innovation: Fostering a culture of continuous innovation encourages the exploration and adoption of new technologies to improve supply chain efficiency.

8. Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Challenge: Increasing consumer and regulatory pressure to reduce the environmental impact of supply chain operations presents a significant challenge for companies.
Solutions:
- Green Supply Chain Practices: Implementing green supply chain practices, such as using renewable energy sources and reducing waste, can improve sustainability.
- Lifecycle Analysis: Conducting lifecycle analysis of products helps identify areas for reducing environmental impact from production to disposal.
- Sustainability Reporting: Regularly reporting on sustainability efforts and progress enhances transparency and accountability.
Case Studies of Successful Supply Chain Management
Case Study 1: Zara – Agile Supply Chain
Overview: Zara, a leading fashion retailer, is renowned for its agile supply chain, which allows it to quickly respond to changing fashion trends and consumer demands.
Strategies:
- Vertical Integration: Zara controls a significant portion of its supply chain, from design to production to distribution, allowing for greater flexibility and speed.
- Frequent Inventory Replenishment: Zara’s stores receive new inventory twice a week, enabling them to constantly refresh their offerings and meet current trends.
- Local Sourcing: Zara sources a substantial amount of its production locally, reducing lead times and increasing responsiveness.
Results:
- Reduced Lead Times: Zara’s lead times are significantly shorter than industry averages, enabling it to bring new designs to market quickly.
- High Inventory Turnover: Frequent inventory turnover reduces the risk of excess stock and markdowns.
- Strong Brand Loyalty: Zara’s ability to consistently offer the latest fashions has helped build a loyal customer base.

Case Study 2: Toyota – Lean Manufacturing
Overview: Toyota’s implementation of lean manufacturing principles has revolutionized its supply chain, focusing on waste reduction and continuous improvement.
Strategies:
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Production: Toyota’s JIT production system ensures that materials and components arrive just as they are needed, reducing inventory levels and waste.
- Kaizen (Continuous Improvement): Toyota fosters a culture of continuous improvement, encouraging employees at all levels to identify and address inefficiencies.
- Strong Supplier Relationships: Toyota works closely with its suppliers to ensure quality and timely delivery, often involving them in the improvement process.
Results:
- Operational Efficiency: Toyota’s lean manufacturing approach has led to significant improvements in efficiency and cost reduction.
- High Product Quality: Continuous improvement and close supplier collaboration have contributed to Toyota’s reputation for high-quality vehicles.
- Sustainable Practices: Lean manufacturing principles support sustainability by minimizing waste and resource consumption.
Case Study 3: Amazon – Technology-Driven Supply Chain
Overview: Amazon’s technology-driven supply chain is a key factor in its success as a leading global e-commerce company.
Strategies:
- Automation and Robotics: Amazon’s warehouses are highly automated, using robots to move and sort items, which increases efficiency and accuracy.
- Data Analytics: Amazon leverages data analytics to optimize inventory levels, predict demand, and personalize customer recommendations.
- Same-Day Delivery: Amazon’s extensive logistics network and use of advanced algorithms enable it to offer same-day delivery in many locations.
Results:
- Rapid Order Fulfillment: Amazon’s technology-driven approach allows for rapid and accurate order fulfillment, enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Cost Savings: Automation and data analytics contribute to significant cost savings and operational efficiency.
- Market Leadership: Amazon’s innovative supply chain practices have helped it become a dominant player in the e-commerce market.

Future Trends in Supply Chain Management
1. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning will continue to transform supply chain management by providing deeper insights, automating decision-making, and enhancing predictive capabilities. These technologies can optimize everything from demand forecasting to inventory management to logistics.
2. Blockchain for Enhanced Transparency
Blockchain technology will play a greater role in ensuring transparency and traceability across the supply chain. It can help prevent fraud, ensure compliance, and provide consumers with detailed information about product origins and journeys.
3. Internet of Things (IoT) Integration
The integration of IoT devices will provide real-time data on the location, condition, and status of goods as they move through the supply chain. This will improve visibility, reduce losses, and enhance decision-making.
4. Sustainable Supply Chain Practices
Sustainability will become an even greater focus, with companies adopting more eco-friendly practices and technologies. This includes reducing carbon footprints, optimizing resource usage, and promoting circular supply chains where products are designed for reuse and recycling.

5. Resilience and Risk Management
The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of supply chain resilience. Future supply chains will prioritize flexibility and risk management, with strategies to quickly adapt to disruptions and ensure continuity.
Conclusion
Overcoming challenges in supply chain management requires a multifaceted approach that leverages technology, fosters collaboration, and emphasizes continuous improvement. By adopting innovative strategies and staying agile, companies can not only navigate the complexities of modern supply chains but also turn these challenges into opportunities for growth and competitive advantage. As the landscape of global commerce continues to evolve, those who invest in robust, resilient, and sustainable supply chains will be well-positioned to thrive in the future.